The United Nations region of Northern America contains five countries: Bermuda, Canada, Greenland, Saint Pierre and Miquelon, and the United States of America. The region has an estimated population of 361 million (2017); Canada and the United States account for more than 99 percent of the population in the region.
View the full United States and Canada region reportUnited States and Canada
According to the latest censuses in Canada (2011) and the United States (2010), Christianity, in its various denominations is the most represented religion in both countries (67.28 percent in Canada, and 76 percent in the United States). The unaffiliated category (religious “nones”) shows a continuous increase in both countries. Educational attainment is relatively high compared to other Organization of Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) countries. In 2016, 47.5 percent of 25-34 year-olds completed tertiary education in the United States, while the level of tertiary education in that same age group in Canada was 60.6 percent.
The United States is one of the world’s oldest democracies. The people benefit from a wide variety of liberties, including the rule of law, freedoms of expression, religion, and association. It remains a highly desirable country for immigrants. Political polarization, including matters of immigration, has increased since the 2016 election of Donald Trump as U.S. President.
Canada also enjoys a long tradition of democratic freedoms. When Justin Trudeau won the 2015 Prime Minister national election he created an executive cabinet composed of an equal number of men and women, the first time in Canada’s history. Trudeau campaigned on a promise of reform of the majoritarian electoral system, in which the candidate with the most votes wins, whether or not they capture more than 50 percent of the votes (Freedom House, 2016).
Despite their advanced state of development, disparity of wealth continues to threaten well-being in the region. The overall poverty rate declined between 2015 and 2016 in 24 of the U.S. states, yet the rate of those in extreme poverty increased, representing 45.6 percent of the nation’s poor (United States Census Bureau, 2017; Bialik, 2017). Canada also faces a challenge in poverty reduction, especially among indigenous populations (MacDonald & Wilson, 2013).
Despite persistent challenges, both Canada and the United States are among the most prosperous in the world. Both countries rank among the most generous in foreign aid, with the United States giving 31 billion dollars and Canada giving five billion dollars in total development assistance to other countries in 2015 (Myers, 2016).
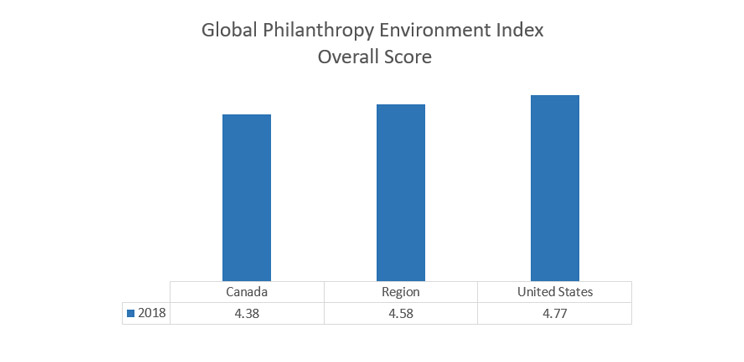
Countries in the region enjoy a highly favorable environment for philanthropy. Both Canada and the United States have a large and diverse philanthropic sector with minimal regulation and high participation in voluntarism and charitable giving.
The region’s government supports nonprofit organizations primarily through favorable tax treatment, service programs that promote volunteering, demand-side funding through grants and contracts, supply-side funding for users of nonprofit services, and public recognition of charitable activities. The government supports philanthropy and relies on it for essential services, healthcare and education in particular.
The region’s donors have grown increasingly sophisticated in their knowledge and expectations of nonprofit organizations. Donors in Canada and the U.S. seek more feedback about the impact of their gifts and organizations’ mission impact, governance, and management. As donors expect more involvement and information, they hold philanthropic organizations accountable to be professional, transparent, responsive, and effective.
New investment vehicles, including online platforms, donor-advised funds, LLCs, and crowdfunding, driven largely by technological change, will drive donor expectations higher and challenge philanthropic organizations accordingly. While the public level of trust in philanthropic organizations is high in the region currently, the sector must continually perform and evolve to maintain its longstanding crucial role in society.